What is the impact of the sun on our eyes?
- News
- 0 Like
- 6669 Views
- 0 Feedback

The sun is a real danger to the eyes because UV rays reach the ocular surface. The vast majority of the rays are absorbed by the cornea and the lens, but some still reach the retina. Long or particularly intense exposure to the sun can cause considerable damage to your eyes:
- Promote AMD, Age-Related Macular Degeneration: degradation of part of the retina that can lead to loss of central vision.
- Increase the risk of cataract: phenomenon of opacification of the lens. Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet rays can increase the risk of developing a cataract prematurely, and thus lead to a progressive decline in vision, accompanied by photophobia (intolerance to light).
- Promote pterygium: a thickening of the tissue, which results in the growth of a skin at the inner corner of the eye and then develops on the rest of the eye. Often pterygium does not cause any symptoms, but if it spreads, it can reach the cornea and thus disrupt vision.
- Catching an " ocular sunburn ": it can occur in several ways. Touching the conjunctiva (photo conjunctivitis), the cornea (photokeratitis), or both (keratoconjunctivitis). This burn is particularly painful and can cause visual disability for 6 to 24 hours. The pain lasts for several days and the eyes are usually swollen and red.
What should I do if I get an eye sunburn?
Like a sunburn on the skin, you won't feel the eye sunburn right away. Usually two to three hours after exposure, the first burning sensations will appear.
For mild ocular sunburns, spontaneous healing is possible within 48 hours. The main symptom is very unpleasant: the sensation of having sunburned eyes. If you have particularly sensitive eyes, have already undergone eye surgery or if the symptoms persist beyond 48 hours, it is advisable to consult your ophthalmologist urgently.
To soothe the pain and treat the eye sunburn, you can use eye drops, gels or ointments. You can also take painkillers.
Children's fragile eyes in the sun
It is important to know that before the age of 1 year, 90% of UVA and more than 50% of UVB reach the retina of babies. Babies should therefore never be exposed directly to the sun without sunglasses or protection (hat, shelter, parasol, etc.)! Between the ages of 1 and 12, 60% of UVA and 25% of UVB rays are not filtered. This is possible because children have a larger pupil and an iris with less pigmentation, as well as a transparent crystalline lens that allows the rays to pass through easily.
Sight is an essential element in a child's development, so it is essential to protect them with suitable sunglasses from an early age. It is with this objective of maximum protection thatHORIZANE has developed a range of sunglasses for babies and children:
- A maximum protection of category 4 / UV 400 (UV 100%).
- Flexible frames for maximum safety: no finger pinching when opening and closing the temples!
- Unbreakable and very resistant lenses made of polycarbonate.
The solution: sunglasses
Sunglasses are PPE: " Individual Protection Equipment ". Each PPE must have a file according to precise standards defined by the Ministry of Industry. The authorities insist that the glasses are really protective and remain so after exposure to the sun. The sunglasses must also have the CE mark and be accompanied by an information leaflet according to ISO 12312-1: 2013 / A1: 2015 and EU Regulation 2016/425.
How to choose your glasses? Which sun filter to choose? Which category?
The solar lens protects at 2 levels: against UV and against light intensity.
UV protection:
For an optimal protection the solar glasses must profit from a protection UV400, otherwise called UV 100%. This is a standard for solar filters. UV400 (or UV 100%) means blocking at least 95% of UVB and 60% of UVA. However, this standard can only be achieved with brown, green or smoke (black) tinted lenses but not with other colours. All sunglasses HORIZANE are equipped with UV400 lenses, which is why we do not offer fancy coloured lenses (except for the capsule collection).
Protection against light intensity
Each pair of glasses must be marked with the protection class corresponding to the filtering capacity of the intensity of the sun's rays. There are five categories classified on a scale of 0 to 4, according to the percentage of light filtered:
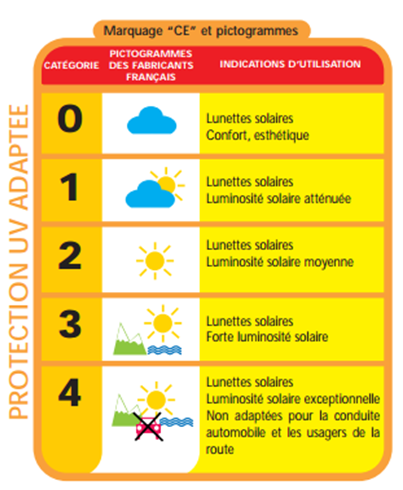
- Category 0 does not protect against solar UV, it is reserved for aesthetics.
- Categories 1 and 2 are suitable for low and medium sunlight.
- Category 3 provides effective protection without obscuring the image in bright sunlight. The HORIZANE Adult glasses are all equipped with category 3 filters.
- Category 4 is essential in situations of high light intensity (snowy mountains or the sea). It protects more effectively against the sun's reflection. It is strongly recommended that children be equipped with sunglasses with this maximum protection filter because their eyes are much more sensitive than those of adults
HORIZANE offers a category 4 filter for its entire children's sunglasses range!
It should be noted that category 4 sunglasses cannot be used when driving because they may blind a driver when driving through a tunnel.
What do polarized lenses provide?
Polarized lenses provide effective protection against UV rays and prevent you from being dazzled by the effect of light reflection. They provide visual comfort that is far superior to conventional sunglasses: colours appear more clearly and contrasts are enhanced. The eyes get less tired, but above all vision is clearer and reliefs are better perceived.




Feedback (0)